|
|
|
|
|
|


|
|
|
|
|
|

Most large files are compressed to speed things up and to make efficient use of space. Multimedia files are very large and are usually compressed for this reason. It is common to download compressed files from the Internet. To compress a file special software is required which will scan the file for repeated patterns in the data. This involves complex mathematical equations and the data scanned will be replaced with smaller codes that take up less room. As an example, the compression software may work by locating all the text characters that are the same and replacing them with a code that will also note the locations of those characters in the data. Pictures can also be compressed by locating for example, all the red pieces, and replacing them with a code. This reduces the file size sometimes by as much as half and is very useful for moving data around the internet as the download time is greatly reduced.
In order for your system to read compressed files, you will require a compatible decompression program that can read these codes and covert the data back into its original format so that you can use the data. When downloading off the Web you may well require a decompression program as many files are compressed on the Internet in order to reserve storage space on servers. Most files that are compressed on the Web will be text, graphics, audio or video files. The most common compressed files will have extensions like .zip, .sit, .tar. These are popular formats for the PC, Macintosh, and UNIX.
The compressed files may be single files or groups of files that have been bundled together into a single archive. An archive file can sometimes contain video or graphics files within it and often contains software programs with related documentation.
To decompress a .zip file you will need a utility like WinZIP or PKUNZIP, which can be downloaded themselves from the Internet. Download the latest version from the home page.
To unstuff a file with a .sit extension, a program called StuffIt Expander will be required and is a popular program for the Mac. Though PKZIP will not decompress files that have been stuffed, there is a StuffIt Expander version for Windows that does. StuffIt Expander can also decompress other formats, including .zip.
Files that have a .sea or .exe extension are self-extracting files for the Macintosh and Windows, which means they do not require additional software to run. You simply click on the file icon to launch it.
home page.
To unstuff a file with a .sit extension, a program called StuffIt Expander will be required and is a popular program for the Mac. Though PKZIP will not decompress files that have been stuffed, there is a StuffIt Expander version for Windows that does. StuffIt Expander can also decompress other formats, including .zip.
Files that have a .sea or .exe extension are self-extracting files for the Macintosh and Windows, which means they do not require additional software to run. You simply click on the file icon to launch it.
It is useful to put a compressed file in its own directory and decompress it into that directory so you can then take note of what has come out of the compressed file.
A compressed drive is not a real disk drive, although it appears like one. The contents of a compressed drive are stored in a single file called a compressed volume file (CVF), which is located on an uncompressed drive called a host drive.
When a hard dive such as the C drive is compressed a new drive letter is assigned to it, such as H. Drive H becomes the host drive for drive C. The compressor then compresses the hard disk into a compressed volume file stored on drive H. The compressed volume file on drive H appears as your original drive C, but drive C has more free space than before. When a drive has been compressed it will increase the total capacity of the drive and give you more hard disk space.
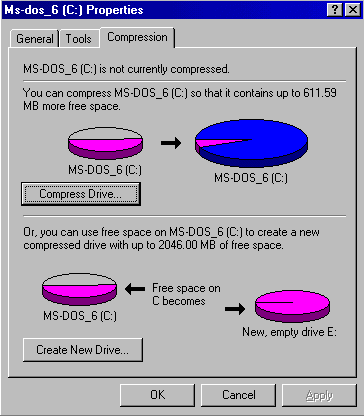
It is also possible to create a new compressed drive using the free space on your drive as the screen print shows above. Instead of compressing the whole of drive C, you could use 10 MB of free space to create a new drive, drive E. Drive E using the compressor above will contain approximately 20 MB of free space
When the operating system attempts to save a file to disk, the compression tool intercepts it and compresses it. When the operating system attempts to open a file, the disk compression utility intercepts the file, decompresses it, and then passes it to the operating system. The entire process should appear transparent to the user although it does have its drawbacks as the process of opening and saving files can be slowed down.
MPEG - Moving Picture Experts Group is a form of compression used for video. MPEG generally produces better quality video than competing formats, such as Video for Windows, Indeo and QuickTime. MPEG files, like any other compressed file, have to be decoded by special hardware or by software.
MPEG achieves high compression rate by storing only the changes from one frame to another, instead of each entire frame. The video information is then encoded using a technique called DCT. MPEG actually removes some of the data but this cannot be detected by the human eye.
There are two main types of MPEG. MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. The newest standard MPEG-2 is used by DVD-ROMs and can compress a 2-hour video into a few gigabytes. There are other types of video compression but MPEG looks as if it will be the one of the future because of its higher quality. MPEG-4 is currently being developed.